Comparing Building Standards from Around the World v2.0

Four months ago, we published our first content request - a comparison of building standards from around the world - which received widespread attention and feedback. After reviewing the feedback, we have updated the report by adding additional standards, increased the number of comparisons and corrected errors.
Change Log
1.
Four new building standards have been added: Passive House Standard, AirRated, Home Performance Index, and HKGBC BEAM PLUS.
2.
"Administrating Entity" has been added. It refers to the legal entity or organization that is in charge of the development and management of the building standard.
3.
"Scoring System" has been changed to "QL (Qualitative)/QT (Quantitative)" to better reflect the differences between the building standards.
4.
Removed details from the "Project Types" table due to too much text. Detailed description is available as a list. "Project Types" content has been updated.
5.
Corrections have been made to previous inaccuracies, including:
- Updated the content in “Introduction”
- Updated the content in "Criteria".
- Updated the content in "Modularization".
- Renamed "China CABR" to "China Green Building Standard".
- Renamed "Data Service" to "Data Audit" and updated the content.
To see the first version, please click here.
This report compares 19 of some of the most widely recognized and used green building standards in the current markets. Each standard is compared and summarized in multiple aspects, including criteria, data requirements, project type, etc. This report can provide a basic guideline when choosing building standards and also give a clearer understanding of the similarities and differences between each standard.
The following table shows a summary of all the building standards and how the comparison is performed:
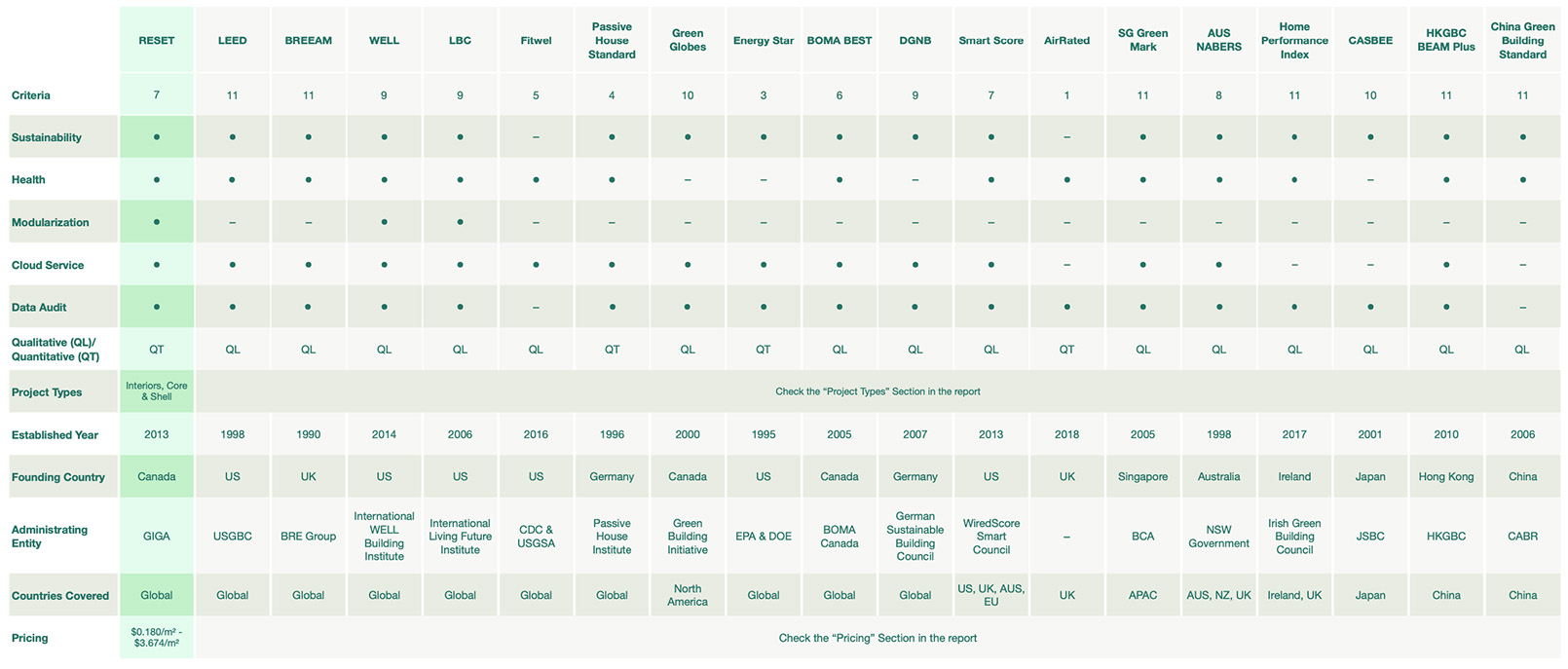
Table 1: Comparison overview of building standards. (Note: To see the table more clearly, Right Click > View Image or zoom in on mobile.)
Introduction
Let's start with a brief introduction of each building standard (text taken from the corresponding standard's website when available or relevant):
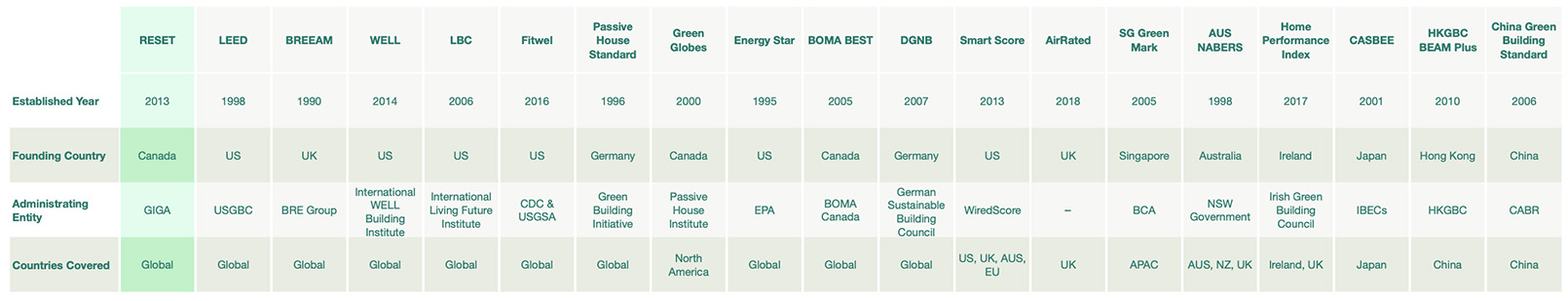
Table 2: Background comparison of building standards. (Note: To see the table more clearly, Right Click > View Image or zoom in on mobile.)
RESET: developed and administrated by GIGA; a performance-driven building standard; founded in Canada in 2013; globally certified projects;
LEED: developed and administrated by the USGBC; a green building standard; founded in the US in 1998; globally certified projects;
BREEAM: developed and administrated by the BRE Group; a green building standard; founded in the UK in 1990; globally certified projects;
WELL: developed and administrated by the International WELL Building Institute; a healthy building standard; founded in the US in 2014; globally certified projects;
LBC: developed and administrated by the International Living Future Institute; a green building standard; founded in the US in 2006; globally certified projects;
Fitwel: developed and administrated by the CDC and USGSA; a healthy building standard; founded in the US in 2016; globally certified projects;
Passive House Standard: developed and administrated by the Passive House Institute; a standard for passive house; founded in Germany in 1996; globally certified projects;
Green Globes: developed and administrated by the Green Building Initiative; a green building standard; founded in Canada in 2000; mainly leveraged in North America;
Energy Star: developed and administrated by the EPA and DOE; a energy standard; founded in the US in 1995; globally certified projects and products;
BOMA BEST: developed and administrated by BOMA Canada; a green building standard; founded in 2005 in Canada; globally certified projects;
DGNB: developed and administrated by the German Sustainable Building Council; a green building standard; founded in Germany in 2007; globally certified projects;
SmartScore: developed and administrated by the WiredScore Smart Council; a smart building standard; founded in the US in 2013; mainly leveraged in the US, EU, and APAC;
AirRated: a standard for indoor air quality; founded in the UK in 2018; mainly leveraged in the UK;
SG Green Marks: developed and administrated by the BCA; a green building standard; founded in Singapore in 2005; mainly leveraged in Asia Pacific;
AUS NABERS: administrated by the NSW gorvernment; a green building standard; founded in Australia in 1998; mainly leveraged in Australia, New Zealand, and the UK;
Home Performance Index: developed and administrated by the Irish Green Building Council; a green building standard for residential buildings; founded in Ireland in 2017; mainly leveraged in Ireland and UK;
CASBEE: developed by the JSBC; a green building standard; founded in Japan in 2001; mainly leveraged in Japan;
HKGBC BEAM Plus: developed and administrated by the HKGBC; founded in Hong Kong in 2010; mainly leveraged in Hong Kong;
China Green Building Standard: developed and administrated by the China Academy of Building Research (CABR); a green building standard; founded in China in 2006; mainly leveraged in China.
Sustainability & Health
Green building standards mainly focus on two aspects: sustainability and health. Some standards might focus on one or the other, while others will do both. A standard will have a sustainability focus if it takes into account environmental performance, while it will have a health focus if it takes into account the health performance of buildings.
The following table lists whether or not a standard focuses on sustainability and/or health:
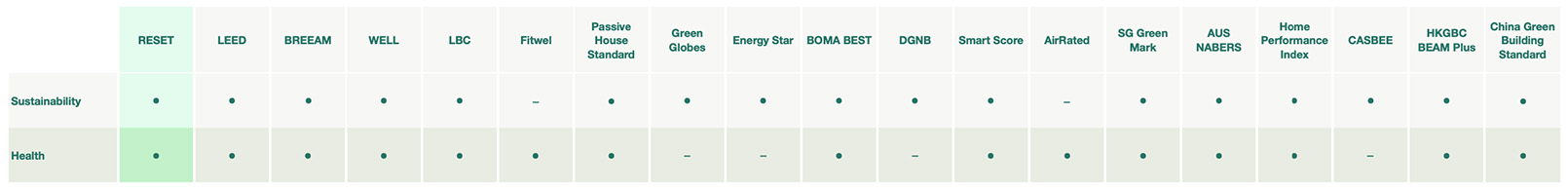
Table 3: Sustainability & Health comparison of building standards. (Note: To see the table more clearly, Right Click > View Image or zoom in on mobile.)
Criteria
Criteria refers to the criteria for which building performance is reviewed by each standard. Due to the different emphasis of each building standard, each standard will consist of different criteria. The following table contains the most typical criteria and compares a summary of the criteria audited by every standard:
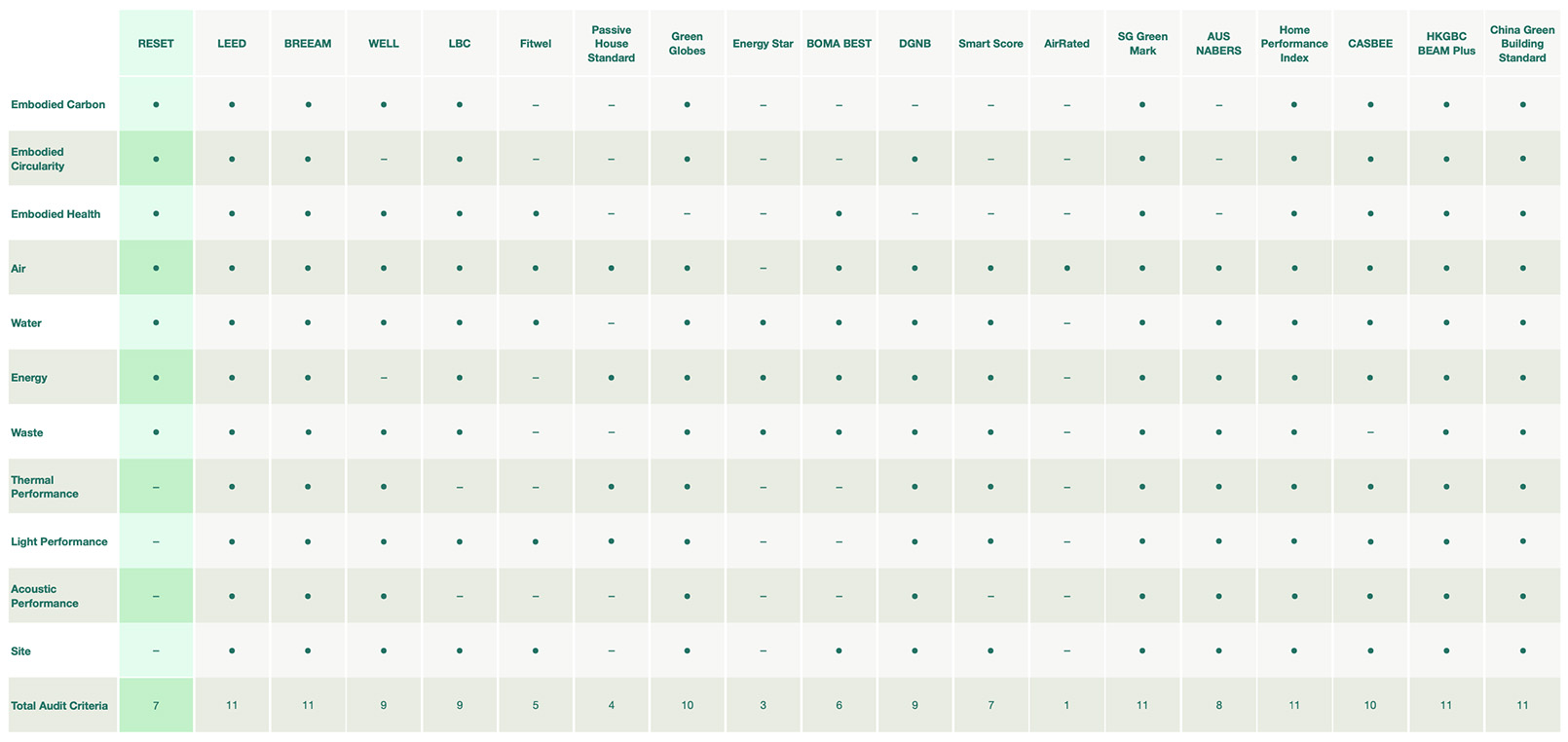
Table 4: Criteria comparison of building standards. (Note: To see the table more clearly, Right Click > View Image or zoom in on mobile.)
Embodied Carbon: Embodied Carbon consists of the GHG emissions associated with building construction, including those that arise from extracting, transporting, manufacturing, and installing building materials on site, as well as the maintenance and end-of-life emissions associated with those materials;
Embodied Circularity: Embodied Circularity refers to the end-of-life and source-of-life of materials used; inclusive of recycled content, sustainably harvested bio-based content, biodegradability and recyclability;
Embodied Health: Embodied Health refers to the impact of the material ingredients on human health, including VOC emissions and material ingredients;
Air: Air refers to indoor air quality, including indicators such as CO₂, PM2.5, TVOC, etc;
Water: Water refers to anything water related, including water consumption and water quality;
Energy: Energy refers to anything energy related, including energy consumption and production locally;
Waste: Waste refers to anything waste related, including the amount of waste generated;
Thermal Performance: Thermal Performance refers to the thermal insulation performance, often including its influence on occupants;
Light Performance: Light Performance refers to the lighting condition, often including its influence on occupants;
Acoustic Performance: Acoustic Performance refers to the sound insulation performance, often including its influence on occupants;
Site: Site refers to the project's ecological situation, traffic situation, etc.
Modularization
Modularization refers to whether customers can freely pick and choose certification criteria from the standard according to their project situation, funding situation, goals, etc.
The following table compares whether each standard has modularization options:

Table 5: Modularization comparison of building standards. (Note: To see the table more clearly, Right Click > View Image or zoom in on mobile.)
Only RESET, WELL and LBC have modularization options. For RESET, there are 7 separate standards and users can freely choose which standard they want to implement and audit according to their own needs. For WELL, a client's pursuit is customized by referencing a library of strategies, WELL Ratings have no mandatory features. For LBC, modularization is based on petals with strict conditions. Currently, optional petals include the water petal, the energy petal, and the material petal.
The rest of the standards do not have modularization options. Clients need to select standards based on building attributes and project type accordingly, for which certification criteria and requirements will be different.
Cloud Service
Cloud Service refers to whether or not there is an online platform provided by the standard for project registration, document submission, performance data viewing, etc.
The table below summarizes and compares whether the standards offer a cloud service:

Table 6: Cloud service comparison of building standards. (Note: To see the table more clearly, Right Click > View Image or zoom in on mobile.)
All mainstream international standards have online cloud services except for AirRated, Home Performance Index, CASBEE, and China Green Building Standard.
Data Audit
Data Audit refers to whether standards need to audit the performance data of projects to achieve certification.
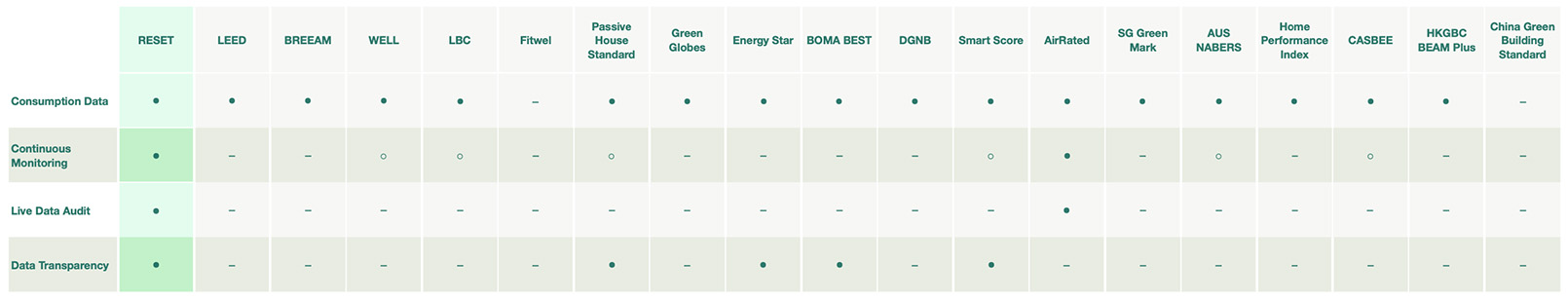
● Applicable ○ Optional - Not Applicable
The description of the different data services is explained below:
Consumption Data: Refers to whether standards need to summarize performance data for audit. Is it necessary, optional, or a plus;
Continuous Monitoring: Refers to whether standards require continuous monitoring data for audit. Is it necessary, optional, or a plus;
Live Data Audit: Refers to whether standards audit the live performance data of projects and whether monitors can stream real-time results;
Data Transparency: Refers to whether clients can view or receive real-time performance data from computers or mobile devices to get a better understanding of their buildings.
QL / QT
QL/QT categorizes the standards into qualitative (QL) and quantitative (QT), which are explained as follows:
Qualitative (QL): Refers to standards that prioritizes evaluation of the built environment via a scorecard system. Often paired with a rating system to distinguish between lower and higher points collected on the scorecard. QL standards scores designs, implementations, and process due to lack of access to performance data. Fors some standards, quantifiable indicators may be considered as bonus points.
Quantitative (QT): Refers to standards that prioritizes evaluation of the built environment via the evaluation of performance data. Reviewed and auditied categories are quantifiable with collected data. Relevant performance data from the built environment, often via continuous monitoring, is a necessary requirement for QT standards.
The table below shows whether a standard is primarily qualitative or quantitative:

Table 8: QL/ QT comparison of building standards. (Note: To see the table more clearly, Right Click > View Image or zoom in on mobile.)
Below is a brief introduction to the properties and rating levels if applicable:
RESET: QT. Projects are assessed on their continuous monitoring performance data. Rating system consists of: Certified.
LEED: QL. Rating system consists of: Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum;
BREEAM: QL. Rating system consists of: Pass, Good, Very Good, Excellent, and Outstanding;
WELL: QL. Rating system consists of Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum;
LBC: QL. Rating system consists of only Pass or Fail;
Fitwel: QL. Rating system consists of & one-star level, two-star level, and three-star level;
Passive House Standard: QT. Rating system consists of: Classic, Plus, and Premium;
Green Globes: QL. Rating system consists of: One Green Globes, Two Green Globes, Three Green Globes, and Four Green Globes;
Energy Star: QT. Energy Star displays a score for project with no rating system;
BOMA BEST: QL. Rating system consists of: Certified, Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum;
DGNB: QL. Rating system consists of: Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum;
SmartScore: QL. Rating system consists of: Certified, Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum;
AirRated: QT. Performance data is collected for 3 weeks. Data Rating system consists of: Certified, Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum;
SG Green Marks: QL. Rating system consists of: Certified, Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum;
AUS NABERS: QL. Rating system consists of: One-Star, Two-Star, Three-Star, Four-Star, Five-Star, and Six-Star;
Home Performance Index: QL. Rating system consists of: Certified, Silver, and Gold;
CASBEE: QL. Rating system consists of: C, B-, B+, A, and S;
HKGBC BEAM Plus: QL. Rating system consists of: Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum;
China Green Building Standard: QL. Rating system consists of: One-Star, Two-Star, and Three-Star;
Project Types
Project Types describes the different types of built environments that a standard can be applied to.

Table 9: Project type comparison of building standards. (Note: To see the table more clearly, Right Click > View Image or zoom in on mobile.)
Below is a list of all standards and their project types:
RESET: New & Existing Buildings, Commercial Interiors, Core & Shell;
LEED: New Buildings, New Interiors, Existing Buildings and Spaces, Neighborhood Development, Cities and Communities, Residential, Retail;
BREEAM: New Construction, Refurbishment & fit out, In-use, Communities, Infrastructure;
WELL: New & Existing Buildings, Interiors, Core & Shell;
LBC: New Building, Existing Building, Interior, Landscape or Infrastructure;
Fitwel: New Construction, Existing Building;
Passive House Standard: N/A
Green Globes: New Construction, Core & Shell, Sustainable Interiors, Existing Buildings, Multifamily for New Construction, Multifamily for Existing Buildings;
Energy Star: New Homes, Commercial Buildings, Industrial Plants;
BOMA BEST: Office, Enclosed Shopping Centres, Open Air Retail, Light Industrial, Multi-Unit Residential Buildings;
DGNB: New Construction, Renovation and Existing Buildings, Building in Use;
SmartScore: N/A
AirRated: New and Existing Buildings; Interiors;
SG Green Marks: New Data Centres, Existing Data Centres, Transit Station, Existing Schools, District, Restaurants, Supermarkets, Retail, Laboratories, Super Low Energy Buildings, New Non-residential Buildings, Existing Non-residential buildings, New Residential buildings, Existing Residential Buildings;
AUS NABERS: Residential Buildings, Hotels, Office, Data Centres, Public Hospitals, Shopping Centres, Warehouses;
Home Performance Index: Homes;
CASBEE: New Construction, Existing buildings, Renovation, Market Promotion, Commercial Interiors, Temporary Construction, Urban Development, Cities, Residential Buildings;
HKGBC BEAM Plus: New Buildings, Existing Buildings, Interiors, Neighbourhood, Data Centres, Existing Schools;
China Green Building Standard: Public Buildings, Residential Buildings.
Pricing
There are a lot of different rules around pricing, therefore, URL links are provided instead.

Table 10: Pricing comparison of building standards. (Note: To see the table more clearly, Right Click > View Image or zoom in on mobile.)
Pricing URL links for each standard can be found below:
BREEAM: https://files.bregroup.com/breeam/FS021_BREEAM-In-Use_Fee-Sheet.pdf
WELL: https://www.wellcertified.com/certification/v2/pricing
Passive House Standard: There are no centrally fixed prices for certification. Each Certifier calculates their offer so that the expected expenses for meticulous checking of the respective building are covered
Green Globes: https://thegbi.org/green-globes-certification/what-it-costs/
Energy Star: https://www.energystar.gov/buildings/about_us/newsroom/media_faqs
BOMA BEST: https://bomacanada.ca/bomabest/fees/
DGNB: https://www.dgnb-system.de/en/certification/certification-fees/index.php
SmartScore: N/A
AirRated: https://airrated.co/pricing/
SG Green Marks: https://www1.bca.gov.sg/buildsg/sustainability/green-mark-certification-scheme/green-mark-assessment-fees
AUS NABERS: https://www.nabers.gov.au/ratings/pricing
Home Performance Index: https://homeperformanceindex.ie/registration-fees/
CASBEE: N/A
HKGBC BEAM Plus: https://www.hkgbc.org.hk/eng/beam-plus/beam-plus-references/fee/fee.jsp
China Green Building Standard: N/A
This report is a work in progress and we intend to add it to our Resources page in the upcoming future.
In the mean time, if you have any comments or feedback (i.e. mistakes, content you want us to add, etc.), please do not hesitate to let us know by emailing us at info@reset.build.
